Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
In the early 1900s what contributed to the
expansion of New Orleans beyond the Natural Levee?
a. | More effective pumps were invented to drain
swampland. | b. | Houseboats
provided residents with a swamp-friendly living arrangement. | c. | New building materials allowed large homes and buildings to be constructed in
the swamp. | d. | A natural decrease
in the water levels of the Mississippi River allowed residents to move further into the
swamp. |
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the geological name for the paths the
Mississippi River takes as it flows into the Gulf of Mexico?
a. | creeks | b. | drains | c. | passes | d. | streams |
|
|
|
Louisiana Rivers
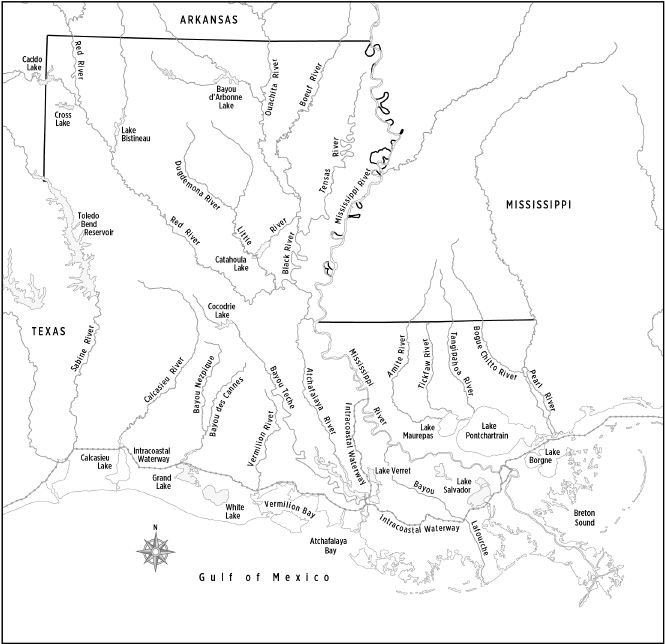
|
|
|
3.
|
Which waterway defines the north eastern boundary
between Louisiana and Mississippi?
a. | Red River | b. | Pearl River | c. | Ouachita
River | d. | Mississippi River |
|
|
|
4.
|
What geographic features define many of
Louisiana’s borders?
a. | hills | b. | mountains | c. | swamps | d. | waterways |
|
|
|
5.
|
What are the three subdivisions of the Mississippi
Floodplain region?
a. | the Passes, the Swamp, and the
Valley | b. | the Blufflands, the Passes, and the
Prairies | c. | the Natural Levee, the Passes, and the
Swamp | d. | the Blufflands, the Natural Levee, and the
Swamp |
|
|
|
6.
|
The Passes 4000 BC-2010 AD
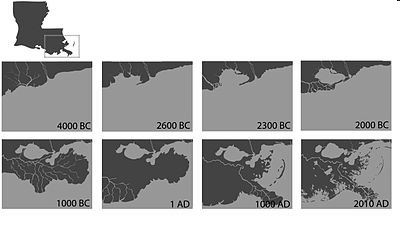
What
conclusion could be drawn from the maps?
a. | The Passes are a stable
ecosystem. | b. | The Passes
continually change and evolve due to the deposits of sediment. | c. | The Passes are not affected when the Mississippi River meets the Gulf of
Mexico. | d. | The Passes are changing because water levels in the Gulf
of Mexico are decreasing. |
|
|
|
7.
|
How did clearing the course of the Red River affect
the development of the Red River Valley?
a. | Easier navigation increased the
population. | b. | Increased flooding
decreased the population. | c. | Faster moving
water removed much of the rich soil farmers desired. | d. | Natural levees were destroyed, drastically altering the course of the
river. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which is a characteristic of the Prairie region of
Louisiana?
a. | tall grasses | b. | piney woods | c. | eroded
bluffs | d. | natural levees |
|
|
|
9.
|
What would happen if a large portion of
Louisiana’s 2.5 million acres of marshland were destroyed?
a. | The shrimping industry would experience a
decline. | b. | The populations of migrating birds would be
decreased. | c. | The absence of
marsh grass would cause the Gulf’s water level to rise. | d. | The abundance of marsh grass would decrease the people’s water
supply. |
|
|
|
Louisiana’s Land Regions
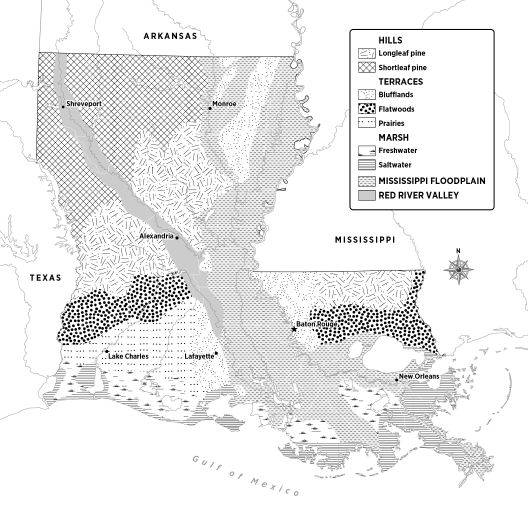
|
|
|
10.
|
Which region lies along Louisiana’s border
with the Gulf of Mexico?
a. | Hills | b. | Marsh | c. | Red River
Valley | d. | Mississippi
Floodplain |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which region covers most of northern
Louisiana?
a. | Hills | b. | Marsh | c. | Mississippi
Floodplain | d. | Red River
Valley |
|
|
|
12.
|
What geographic feature marks the highest point in
Louisiana?
a. | Salt Domes | b. | Mississippi Delta | c. | Driskill
Mountain | d. | Red River Valley |
|
|
|
13.
|
How is the red soil that dominates the Hills region
related to Louisiana’s agricultural industry?
a. | Farming is not a viable option in this region due to
poor soil. | b. | Farming must be
specialized due to high levels of iron in the soil. | c. | Farming a wide variety of crops is made easy by the nutrient rich
soil. | d. | Farming is not a viable option in this region due to
massive soil erosion. |
|
|
|
14.
|
What are the agricultural benefits of alluvial
soil?
a. | It is easily transported by a
river. | b. | It helps to create a natural
levee. | c. | It is deposited along the banks of the Mississippi
River. | d. | It is fertile, produces abundant vegetation, and is well
suited for growing crops. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Why was an extensive flood control system built
along the banks of the Mississippi River?
a. | to collect drinking water | b. | to change the course of the river | c. | to keep the river from flooding ever again | d. | to protect the cities along the river’s
course |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the name of the system of man-made canals
that link waterways from the Atlantic Ocean in Florida all the way to the Gulf of
Mexico?
a. | Aquatic Highway | b. | Interstate Canal Corridor | c. | Gulf Intracoastal Waterway | d. | Gulf-Atlantic Transport System |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the main purpose of the Gulf Intercoastal
Waterway?
a. | to reduce commuter traffic between metropolitan
areas | b. | to provide flood control for the coastal plains
region | c. | to link marine habitats and protect endangered
species | d. | to provide a safe and continuous channel for small boats
and ships engaged in trade and commerce |
|
|
|
18.
|
How did the damming of the Sabine River change the
geography of the Hills region?
a. | It caused the river to change
course. | b. | It lowered the overall elevation of the
region. | c. | It stopped the flow of the Sabine River
completely. | d. | It created a giant
lake known as the Toledo Bend Reservoir. |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the largest natural lake in
Louisiana?
a. | Grand Lake | b. | Lake Charles | c. | Lake
Pontchartrain | d. | Toledo
Bend |
|
|
|
20.
|
How did channel construction affect Lake
Charles?
a. | Connecting Louisiana’s waterways had no effect on
the lake. | b. | Connecting to other waterways had a negative impact on
sport fishing. | c. | Connecting to
other waterways caused the water level in Lake Charles to noticeably
decrease. | d. | Connecting Lake Charles to other waterways helped its
port to become one of the largest in the state. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.
|
If it is 10:00 AM in Louisiana, what time is it in
Alaska?
a. | 1:00 PM | b. | 2:00 PM | c. | 6:00
AM | d. | 7:00 AM |
|
|
|
22.
|
If it is 12:30 PM on Monday in Louisiana, what time
is it in Eastern Australia?
a. | 4:30 AM Monday | b. | 4:30 AM Sunday | c. | 4:30 PM
Sunday | d. | 4:30 AM Tuesday |
|
|
|
23.
|
Louisiana Average Annual
Precipitation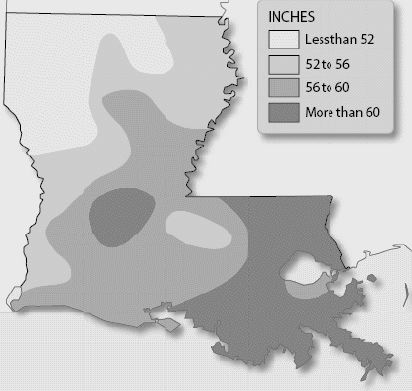 Which region of
Louisiana receives the most rain annually?a. | northeast | b. | northwest | c. | southeast | d. | southwest |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which agricultural industries suffered great losses
following Hurricane Katrina?
a. | citrus, livestock, rice, and
timber | b. | fishing, hunting, livestock, and
rice | c. | citrus, crabbing, hunting, and
timber | d. | crabbing, fishing, hunting, and
shrimping |
|
|
|
25.
|
The following statement is from the article,
“Eat More Strawberries,” from the LSU Agricultural Center website in 2014.
“Strawberries continue to be the leading fruit crop in the state
(Louisiana) with Tangipahoa Parish as the leading strawberry producing parish with $11.5 million in
sales during 2010.”
What conclusion can
be drawn from this statement?
a. | Louisiana’s soil is only good for growing
strawberries. | b. | Strawberry crops
are not affected by flooding and hurricanes. | c. | Consumers love
Louisiana strawberries more than those from other states. | d. | The state’s early spring is a great economic advantage for Louisiana
farmers. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which has been responsible for damaging
Louisiana’s coastal regions?
a. | earthquakes | b. | hurricanes | c. | tsunamis | d. | volcanoes |
|
|
|
27.
|
Why was the Old River Control Structure built in
1963?
a. | It serves as a dock for boats traveling the
Mississippi. | b. | It is a station
used to regulate boat traffic on the Mississippi. | c. | It collects the rich soil and sediment carried by the Mississippi
River. | d. | It controls flooding and prevents the Mississippi from
changing course. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which is a potential outcome if the erosion of
Louisiana’s wetlands continues without intervention?
a. | Fish and bird populations would
increase. | b. | Gas prices would decrease across the
nation. | c. | Seafood prices would increase across the
nation. | d. | There would not be any noticeable
consequences. |
|
|
|
29.
|
How is the need to control the flooding of the
Mississippi River related to coastal erosion?
a. | Levees and dams allow humans to control sediment
deposition. | b. | Changing the
river’s course makes the water flow faster into the Gulf. | c. | Silt that would have slowed the process of subsidence is trapped behind
dams. | d. | Silt that would have been deposited along the banks of
the river is diverted to the coast, increasing land area. |
|
|
|
30.
|
How did the extensive canal system though the
coastal wetlands affect the region?
a. | Plant and animal life flourished due to reduced
flooding. | b. | Farming land area was increased due to controlled
flooding | c. | Marsh grasses were lost as saltwater moved into
freshwater marshes. | d. | Directed water
flow eliminated areas of brackish water, reducing some fish
populations. |
|